Studies of Apatite Chemistry
|
Studies of Apatite Chemistry |
|
|
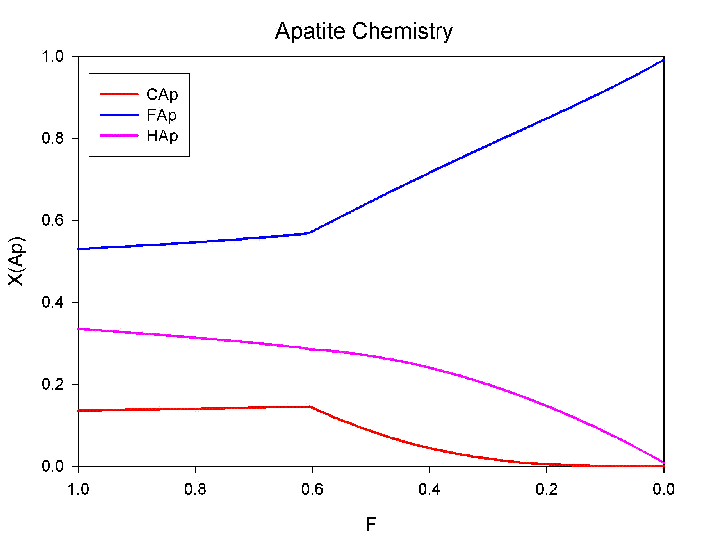 Model of the halogen content in apatite crystallizing from a silicate melt. |
Model of the chemistry of apatite crystallizing from a pluton with 4 wt.% initial water, 375 ppm Cl and 400 ppm Cl, at a depth of approximately 6 km (similar to the conditions for emplacement of the equigranular Half Dome granodiorite, Tuolumne Intrusive Suite, Yosemite National Park.. Upon commencement of volatile saturation, the magmatic vapor has approximately 36,000 ppm Cl and 110 ppm F. The Cl/F ratio in apatite decreases with volatile saturation, hovever, the same trend would be exhibited by a simple decrease in temperature with crystallization. A more appropriate indicator of volatile saturation is a reduction in the Cl/OH ratio in apatite, a trend that can't be explained by down temperature processes (Piccoli and Candela, 2002). It is just like cleaning a hot tub: it is not the amount of Cl, but rather the Cl relative to water, that is important!
|
|
[Studies
of Shallow Plutonism][Apatite in Igneous
Systems][Microanalysis] |
|
Maintained by Phil
Piccoli |